|
|
Home »
~e-VIBS »
Our Achievements
OUR ACHIEVEMENTS
At e-VIBS, we believe that every problem has its solution. We developed a systematic research approach to ensure the finding of the solution. Talk to us and we will
help you in getting the right solution you are looking for. We might as well working together with you to ensure an efficient approach in terms of time and cost.
The following are some of our achievements and we are proud of making these contributions especially to the advancement of human kind in the related discipline.
An Accurate and Cost Effective Method for Ground Based Measurement
of Aerosol Optical Depth
Aerosols content in atmosphere is one of the environmental issues both in climate forcing and human health effects. They exert a variety of impacts on climate directly
by interaction with solar terrestrial radiation and on human health because of the pollution in air with particulate matter. Thus, continuous monitoring of aerosol content in air is
vital. Measurement of atmospheric aerosol is typically performed by satellite observation, airborne measurement, and ground-based instruments. Aerosol monitoring using satellite,
airborne, and LiDAR are quite prohibitive with necessary complex and expensive instrumentation. In contrast, ground-based sunphotometer is cost-effective, portable, and has less
complicated measurement algorithms. Unfortunately, frequent calibration of the operating instrument is required to maintain its retrieval accuracy. Conventionally, the existing
calibration method is performed either by absolute calibration or using Langley extrapolation at high altitude. The former method is always complicated by the degradation of the standard
light source. While the main purpose of the latter method performed at high altitude is to obtain homogeneous and stable sky condition but this involves logistics and financial problems.
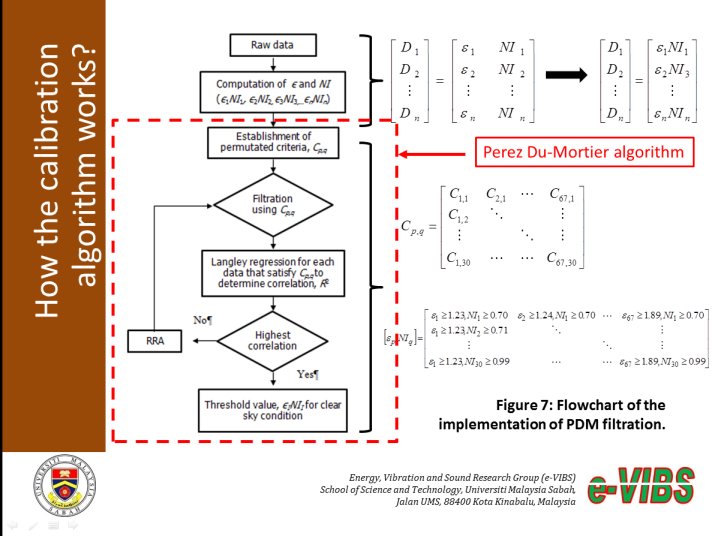
We proposed a solution for these issues is by introducing an objective algorithm for data selection that closely imitates the high altitude clear-sky condition for measurements taken at
low altitudes. For this purpose, Perez and Du Mortier sky classification are used and combined with a statistical filter to ensure ideal clear sky data are selected. Cross reference with
i-SMARTS model in aerosol optical depth value shows a perfect agreement with low uncertainty and comparable to most other studies that performed at high altitude.
Related publications:
- Jackson H.W. Chang,
*Jedol Dayou & Justin Sentian. 2014. Development of near-sea-level calibration algorithm for aerosol optical depth measurement using ground-based spectrometer.
Aerosol and Air Quality Research
.
14(1):386-395.
(ISI Impact Factor in 2011: 2.827).
-
*Jedol Dayou, Jackson Hian Wui Chang, Rubena Yusoff, Ag. Sufiyan Abd. Hamid, Fauziah Sulaiman & Justin Sentian. 2013. Development of Perez-Du Mortier Calibration Algorithm
for Ground-Based Aerosol Optical Depth Measurement with Validation using SMARTS Model.
International Journal of Physical Science and Engineering
.
7(10): 933-938 {
Download File Size 242kB} -
(indexed by International Science Index and Google Scholar).
- Jackson H.W. Chang,
*Jedol Dayou & Justin Sentian. 2013. Investigation of Short Time Scale Variation of Solar Radiation Spectrum in UV, PAR, and NIR Bands due to Atmospheric Aerosol and Water
Vapor.
World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology
.
2013(73): 1112 - 1117 {
Download File Size 490kB} -
(indexed by Scopus).
- Jackson H.W. Chang,
Jedol Dayou & *Justin Sentian. 2013. Diurnal evolution of solar radiation in UV, PAR and NIR bands in high air masses.
Nature Environment and Pollution Technology
.
12(1): 1 - 6 {
Download File Size 307kB} -
(indexed by Scopus).
Increasing the Electrical Power Output From Piezoelectric Harvesting System Using Width-Split Method
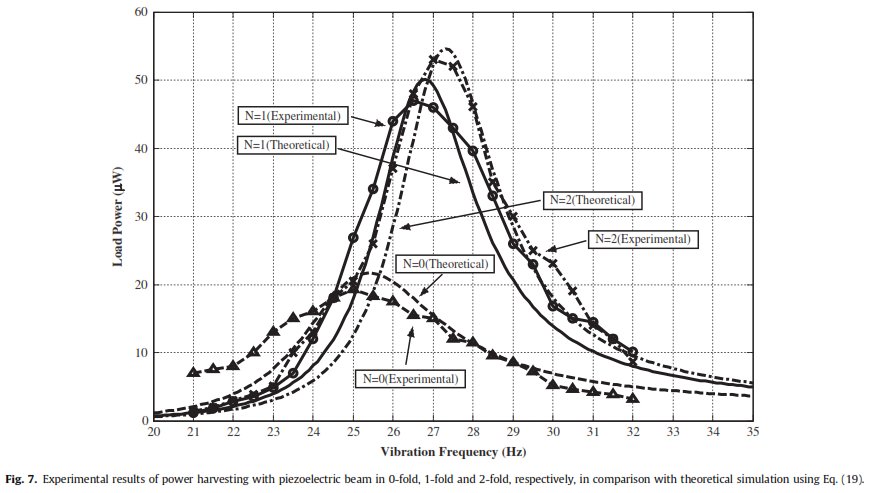
We proposed a simple method to increase the piezoelectric power harvesting from ambient vibration by folding equally and then splitting a given dimension of
piezoelectric material with the pre-defined dimensions so that the conversion of energy is more efficient during the vibration by reducing the viscous damping of the piezoelectric
materials. It can be incorporated with other optimization techniques for maximizing the output power density. The experimental results of this work show that the power harvested increases
145 percent by the first folding and 176 percent by the second folding as compared to power harvested without folding.
Related publications:
- Chow Man Sang, *Jedol Dayou & Willey Y.H. Liew. 2013. Increasing The Output From Piezoelectric Energy Harvester Using Width-Split Method With
Verification.
International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing
.
14(12): 2149-2155
(ISI Impact Factor in 2012: 1.585, Q1 journal in Industrial and Manufacturing Engineering).
- *Jedol Dayou, W.Y.H. Liew & Man-Sang, C. 2012. Increasing the bandwidth of the width-split piezoelectric energy harvester.
Microelectronics Journal
.
43: 484 - 491
(ISI impact factor in 2011: 0.919) {
Download File Size 656kB}.
-
*Jedol Dayou, Chow Man Sang & W.Y.H. Liew. 2011. Harvesting electric charges from ambient vibration using piezoelectric.
Borneo Science
.
29: 23 - 31 {
Download File Size 297kB}.
-
*Jedol Dayou & Man-Sang, C. 2011. Performance Study of Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting to Flash a LED.
International Journal of Renewable Energy Research
.
1(4): 323-332. {
Download File Size 496kB} -
(indexed by Google Scholar).
-
*Jedol Dayou, Man-Sang, C., Dalimin, M. N. & Wang, S. 2009. Generating electricity using piezoelectric material.
Borneo Science
24:47-51 {
Download File Size 140kB}
Introducing the Ideal Band-pass Filter for Mode Shape Reconstruction of an Impulse Excited Structure
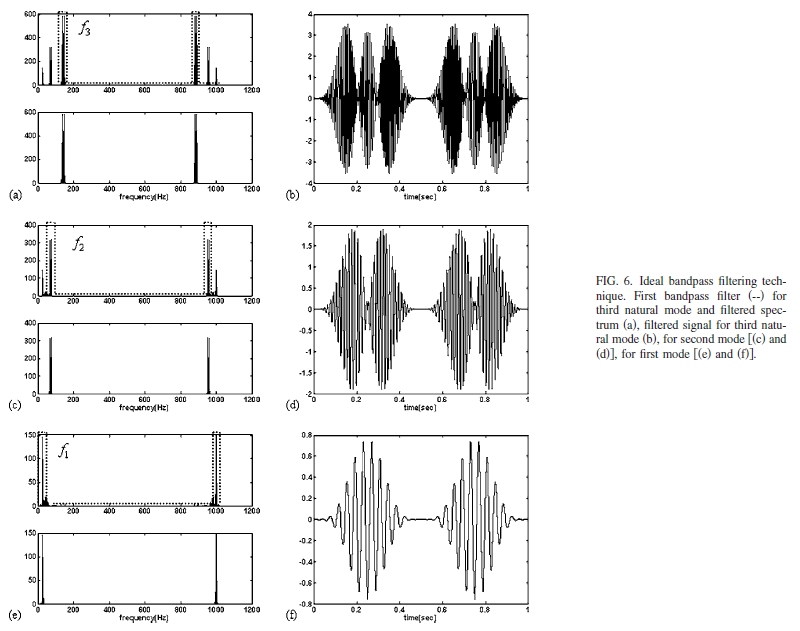
The Hilbert-Huang transform was used to develop the mode shape reconstruction in vibration testing using continuous scanning laser Doppler vibrometer (CSLDV) and empirical mode
decomposition. However, the mode shape reconstruction process suffers a great setback due to the interference of frequency components other than the frequency of interest. Although
theoretically the interference can be removed using conventional bandpass filter, there is another great setback as the conventional filter suffer from phase shifting problem which could
confuse the sign determination and coordinate-trajectory matching. In order to overcome this problem, an innovative step of using ideal bandpass filters was introduced. As a result, the
Hilbert-Huang transformation can be used to recreate almost perfect structural mode shape even in the impact excitation case. The work was carried out at
Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology, South Korea together with
Prof. Dr. Semyung Wang of
Intelligent System Design Laboratory
Related publications:
- Yongsoo Kyong, Daesung Kim,
Jedol Dayou, Kyihwan Park & Semyung Wang. 2008. Mode shape reconstruction of an impulse excited structure using continuous scanning laser Doppler vibrometer and empirical
mode decomposition.
Review of Scientific Instruments
79(7): 075103(12pages)
(ISI Impact factor: 1.738) {
Download File Size 1,061kB}.
- Kyong, Y., Kim, D.,
Jedol Dayou, Park, K., and Wang, S. 2008. Mode shape reconstruction using CSLDV and HHT.
15th International Congress on Sound and Vibration. 6-10 July 2008, Daejeon, South Korea.
- Yongsoo Kyong, Daesung Kim,
Jedol Dayou, Kyihwan Park, Semyung Wang. 2008. Mode shape reconstruction of a structure using HHT and CSLDV.
Annual Spring Conference of the Korean Society of Mechanical Engineers - Dynamics and Control Division. 6-9 May 2008, Yeungnam University, South Korea.
- Yongsoo Kyong, Daesung Kim,
Jedol Dayou, Kyihwan Park & Semyung Wang. 2008. Mode shape reconstruction of an impulse excited structure using HHT and CSLDV.
Annual Spring Conference of the Korean Society for Noise and Vibration Engineering. 17-18 April 2008, Hoengseong-gun, Gangwon-do, South Korea.
New Application of the Fixed-Points Theory
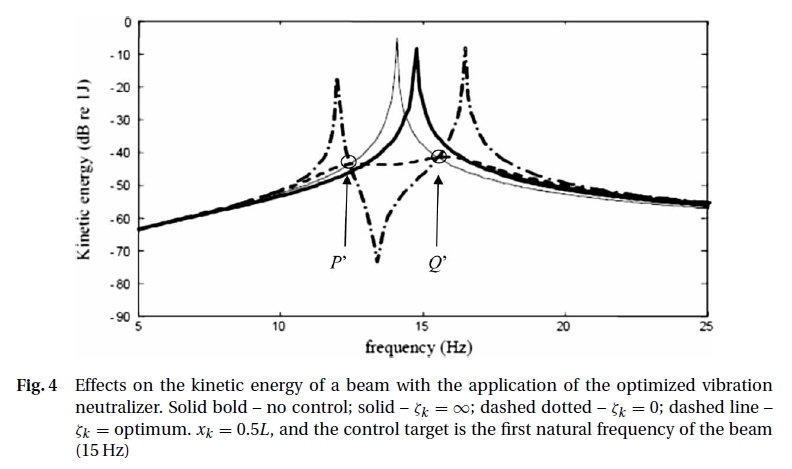
The fixed-points theory has its root dating back to 1932 by Hahnkamm. Since then, it has been used in many applications as one of the design laws in fabricating a vibration
neutralizer for relatively simple structures. We reformulated the theory to be applied in global vibration control of complex body such as beams and plates. Part of the work was developed
at
Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology, South Korea together with
Prof. Dr. Semyung Wang of
Intelligent System Design Laboratory
Related publications:
-
Jedol Dayou. 2010. The Fixed-points theory revisited with new application.
Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C, Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science
.
224(C8): 1627-1634. DOI: 10.1243/09544062JMES1895
(ISI Impact Factor: 0.451) {
Download File Size 264kB}.
-
*Jedol Dayou & Semyung Wang. 2006. Derivation of the fixed-points theory with some numerical simulations for global vibration control of structure with closely spaced natural
frequencies.
Mechanics Based Design of Structures and Machines
36(1): 49 - 68
(ISI Impact factor: 0.326) {
Download File Size 1,538kB}.
-
*Jedol Dayou. 2006. Fixed points theory for global vibration control using vibration neutralizer.
Journal of Sound and Vibration
292(3-5): 765 - 776
(ISI Impact factor: 0.884) {
Download File Size 452kB}.
-
*Jedol Dayou. 2005. A new application of the Fixed-Points theory for the control of kinetic energy of a continuous structure.
International Journal of Acoustics and Vibration
10(4): 170-174 -
(indexed by Scopus). {
Download File Size 329kB}.
Active-Passive Analogy
Prior to the establishment of e-VIBS, Dr. Jedol Dayou, together with
Prof. Dr. Micheal John Brennan (formally with ISVR now at Departamento de Engenhaira Mecanica,
Universidade Estadual Paulista "Julio De Mesquita Filho") have developed the active-passive vibration control analogy. In this analogy, he successfully established a procedure to make use
the well-known active vibration control method to determine the parameters of vibration neutralizers that minimizes the vibration amplitude of a structure. Using this method, the control
performance of the passive control device can be made comparable to its active control counterpart.

Related publications:
-
*Jedol Dayou. 2003. Determination of the optimal tuning ratio of a tunable vibration neutralizer using quadratic minimization technique.
Jurnal Fizik Malaysia
24(3&4): 155 - 159 - {
Download File Size 3379kB}.
-
Jedol Dayou & M. J. Brennan. 2003. Experimental verification of the optimal tuning of a tunable vibration neutralizer for global vibration control.
Applied Acoustics.
64(3): 311 - 323
(ISI Impact factor: 0.464).{
Download File Size 306kB}
-
Jedol Dayou & M. J. Brennan. 2002. Global control of structural vibration using multiple tuned tunable vibration neutralizers.
Journal of Sound and Vibration
258(2): 345 - 357
(ISI Impact factor: 0.829). {
Download File Size 306kB}
-
J. Dayou & M. J. Brennan. 2001. Optimum tuning of a vibration neutralizer for global vibration control.
Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C, Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science
215(8): 933 - 942
(ISI Impact factor: 0.326).
- *M. J. Brennan &
Jedol Dayou 2001. Global control of vibration using a tunable vibration neutralizers.
Noise and Vibration Worldwide
32(5): 16 - 23 -
(indexed by Scopus) {
Download File Size 306kB}
- M. J. Brennan &
J. Dayou 2000. Global control of vibration using a tunable vibration neutralizer.
Journal of Sound and Vibration.
232(3): 585-600
(ISI Impact factor: 0.799). {
Download File Size 366kB}
updated on 2022-01-23 11:45:10 by Jedol Dayou, Assoc. Prof. Dr
|





